How do you write a product SWOT analysis?

SWOT analysis is one of the first steps in any marketing research exercise. The acronym SWOT lists down the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the business on a microscopic level. As business students, you must know when and how to apply SWOT insights when researching a product or service.
In fact, SWOT is a vital aspect of situational analysis, presenting the immediate internal and external factors affecting the brand. The strengths and weaknesses of the products are the internal factors, i.e. directly under the marketer’s control. Opportunities and threats are external factors that determine the market environment.
If you are looking for some help with your next business studies assignment on SWOT analysis, then I got you covered! Here is a stepwise guide on how to document a SWOT report below.
Step 1: Specify your business goals
It is essential to specify your objectives, the nature and purpose of your product before you create a SWOT report on it. Begin the SWOT report with a brief outline of the brand. This would include specific questions like
- What is the business about?
- What is the main product or service you deal with?
- What is the reason behind this SWOT analysis?
- Who is your core customer base?
- How do you plan to use this report to improve your brand?
These questions tell you about what, how, and why is the SWOT research necessary to your product.
Step 2: Collect information
Once you have the primary objectives and reasons for the SWOT ready, you can move on to the next level. This is where you collect all available data, conduct market surveys and customer behaviour studies.
Here, you can refer to previous research papers and findings as well. Ensure that you cite these resources properly to avoid risks of intellectual theft. I also recommend students to check the credibility of the source before borrowing from it.
Customer preferences, buying trends and demand patterns shape your product marketing strategy. It helps you identify the earning opportunities and risks involved in the industry.
The weaknesses are the disadvantages the product has when it enters the market
Step 3: Categorize data
Most marketing case studies give you information about the product and its place in the market. As business students, you must learn how to sort and filter out this information to get the required insights from it.
As per the SWOT analysis, you can divide the information into four main categories- strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. I will discuss the details of these four sections later in the blog. As for now, understand that all the marketing data you collect is sorted in either of these categories.
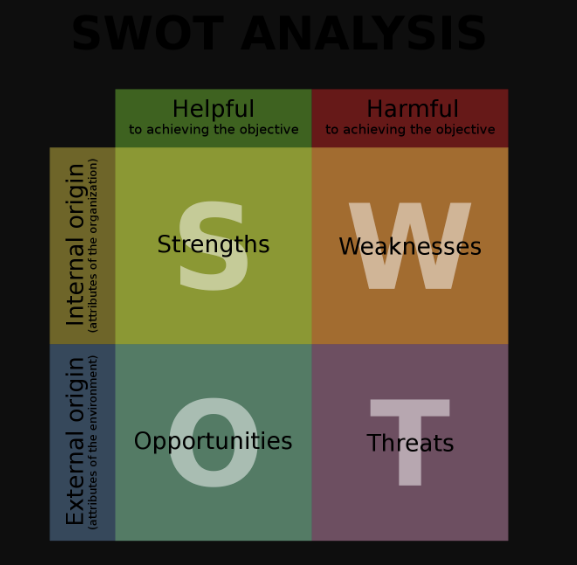
Step 4: Data analysis and sorting
The next step is data analysis, where you try to arrange the information in ways that reveal interesting insights. Sorting the report as per the SWOT guidelines is a very meticulous process. A straightforward way to organize data is by creating a checklist.
Understand some elements can fall under both strengths and weaknesses in the SWOT report. Similarly, there is a fine line between opportunities and threats.
Step 5: Identify your strengths
The first part of the SWOT analysis is identifying the advantages of the product. This is where you list the strong points of the brand. For most business assignments, students have the liberty to choose their product or service
You can also create an entirely fictional brand from scratch or refer to a case study for your preliminary data. You can refer to this paper on SWOT analysis- a theoretical review for identifying the strengths of your product are.
- Capital investment and cashflow
- Growth and profit turnover
- Skilled management
- Strong inventory management
- Increasing customer demand
- An accurate and robust balance sheet
- Good credit rating
- Great marketing team
- Effective online presence
You can talk about these aspects and more depending on the sector. Note that, you don’t have any personal bias or subjective opinion in this process. Keep your analysis objective and entirely from a third-person narrative.
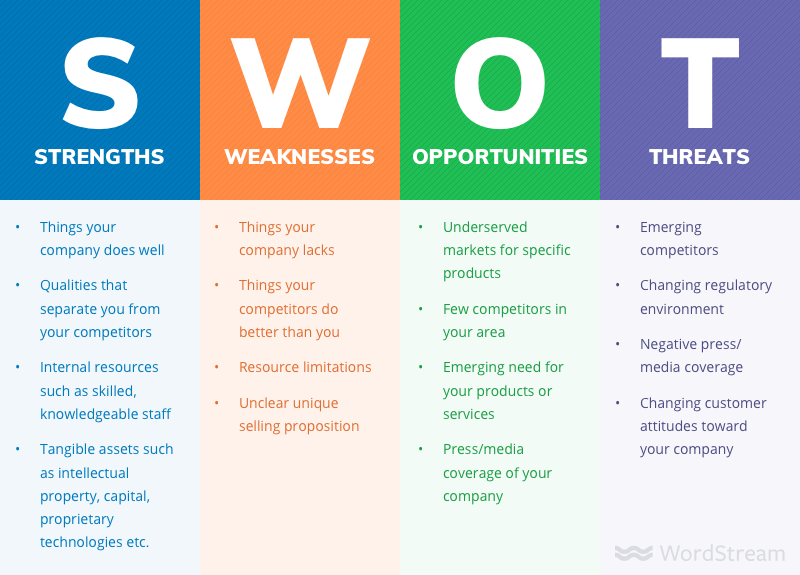
Step 6: Find out the core weaknesses
The weaknesses are the disadvantages the product has when it enters the market. These weaknesses are usually internal in nature and can be rectified. The purpose of the SWOT report is to highlight these cons and suggest effective remedies to improve them. Refer to this chapter on SWOT analysis to identify these common weaknesses and more
- Inadequate funding
- Lack of investment
- Unclear brand image
- Poor product quality
- Ineffective or impractical packaging
- Inefficient marketing team
- Bad website
- Stagnancy in brand image
- Poor market research
I would again repeat that students should be careful to keep the SWOT analysis objective and orderly
Step 7: Explore the opportunities
The other two factors in the SWOT analysis- opportunities and threats- are entirely external. However, a change in company or product policies can indirectly affect these factors. Students with the SWOT report learn to read the market and the opportunities looming ahead
Refer to this paper on the practical application of SWOT analysis for more details. Here are some opportunities you can discuss
- Weak competition
- Change in demand trends
- The decrease in production prices
- A shift in technology
- A new trend or tool introduced
- Changing customer behaviour
- Political or social change
- Cultural shift or a distinct difference in ideology
- Social media trends and hashtags
An aspiring entrepreneur must learn to predict market trends and optimize them. The peers and other companies in the industry add on to the sense of urgency. The sooner you recognize these trends, the better off your product is in the face of intense competition.
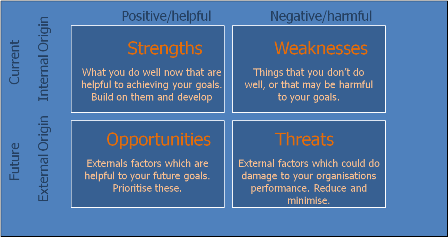
Step 8: Risk estimation
The last part of the SWOT analysis is- threats. This refers to the risks and loss of revenue that one predicts in the foreseeable future. Now, opportunities and threats are not 100% accurate as you never know how the market dynamics can shift over time. Here are some risks you can highlight with the SWOT analysis.
- Legal or copyright issues with the product
- Intellectual theft and accusations of plagiarism
- Loss of demand
- Increase in competition
- New companies entering the market
- Increase in cost of production
- Political social or economic instability
The more you read the market and the prevalent trends, the better you predict the future based on those insights. An estimation of threats prepares the product to overcome any obstacle with relatively more success.
Step 9: Drafting the report
After sorting and analyzing each aspect of the SWOT report, you can predict how the product will fare in the market. With SWOT, students understand how the industry dynamics work on a very superficial level. It is important to note that SWOT doesn’t present a holistic picture,
The report should follow a conventional structure of a proper introduction, middle and ending. Begin the report by setting your product in its core sector and defining your customer base. This section gives the reader some context about the brand and its position in the market.
The body of the report is where you list the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with the product. I would suggest students to use infographics and charts to present this data in an organized format.
The conclusion is where you suggest ways to capitalize on the strengths and opportunities. It also gives you the space to address the weaknesses and threats. Ensure that you use other research methods like PESTLE and Porter’s five forces etc. to outline the business environment and competition.

Step 10: SWOT checklist
Before you submit the final draft, it is crucial to run it by a list. It ensures that you cover all the aspects of the SWOT analysis and do miss out on anything vital. With a SWOT, you get a chance to delve deep and demonstrate how to utilize the information in the best possible way. Here is a SWOT checklist
- Consult your peers and professors about the structure of the SWOT report
- Ensure that the information collected is accurate
- Consider the strengths and weaknesses via the internal sources like marketing strategies, management and more.
- Also, you must estimate the risks and opportunities using external elements that financial climate, competitors, customer behaviour etc.
- Review the SWOT insights using analysis tools and platforms. Then come up with actionable solutions to improve your product value.
Use Infographics and charts to present the data in an organized format
Step 11: Don’t stop at SWOT
SWOT analysis usually gives a very surface reading of the market and your business. It is the first step in market research that tells you about the industry potential and profit margin. With SWOT you know how the brand/product stands in the current market scenario
However, SWOT is a microscopic approach. It doesn’t consider the macro factors like socio-political stability, environmental factors, and legal aspects of the business. This is where PESLTEL analysis comes into the picture.
Quick links and references
SWOT analysis of a product- Sample
The bottom line
Conducting a SWOT analysis is easier said than done. There are a lot of elements you need to consider and take care of. In most business assignments, you might have to develop a detailed SWOT report for a particular product or brand.
This requires a very niche approach, and I hope this stepwise guide would help you with it. Good luck!



